Materiality
Tata Steel prioritises stakeholders, using periodic materiality assessments to understand and address their needs and concerns effectively.
Since FY2012-13, Tata Steel has been conducting periodic materiality assessments every three years to understand key stakeholder issues and focus areas to prioritise the Company’s risks and opportunities. The last assessment was conducted in FY2022-23.
Materiality assessment is a detailed exercise that covers stakeholders from all operating geographies — India, Thailand, the Netherlands, and the UK — and the identified risks and opportunities help in developing the Company’s strategy over the short, medium, and long term. The assessment also facilitates deeper stakeholder engagement and incorporates their feedback on the Company’s roadmap, regularly reviewed by Tata Steel’s senior leadership and the Board of Directors.
The risks arising out of material issues are assessed as per the organisation’s Enterprise Risk Management process and framework.
In accordance with the AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard, Tata Steel identifies the following as its stakeholders:
- Senior Management
- Investors (Debt & Equity)
- Employees
- Contractual Workforce
- Community
- Suppliers
- Customers
- Media
- Regulatory Bodies
- Industry Bodies
- Non-government organisations
The last materiality assessment, conducted in FY2022-23, was undertaken on a consolidated basis through a structured stakeholder consultation by an independent agency, according to best-in-class international practices. It has helped Tata Steel identify the top 15 ESG issues, material to its business and is integral to its vision of being the global steel industry benchmark for Value Creation and Corporate Citizenship. The assessment is aligned with the guidance from International Standard Setting Bodies, including but not limited to Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) and the Integrated Reporting <<IR>> Framework, covering both general standards and sector-specific standards related to iron and steel, and metals and mining industries. Material topics are further linked to the requirements of GRI, SASB, World Steel Association (WSA), Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR), and World Economic Forum (WEF).
There are two aspects to Tata Steel’s materiality assessment:
- Impact Materiality: Determined by the scale, scope, and irreversible nature of the impact, this factor considers the effects on both people and the environment.
- Financial Materiality: Determined by the risks and opportunities, this factor considers the impact on the organisation’s financials.
The materiality assessment exercise is an 8-step process:
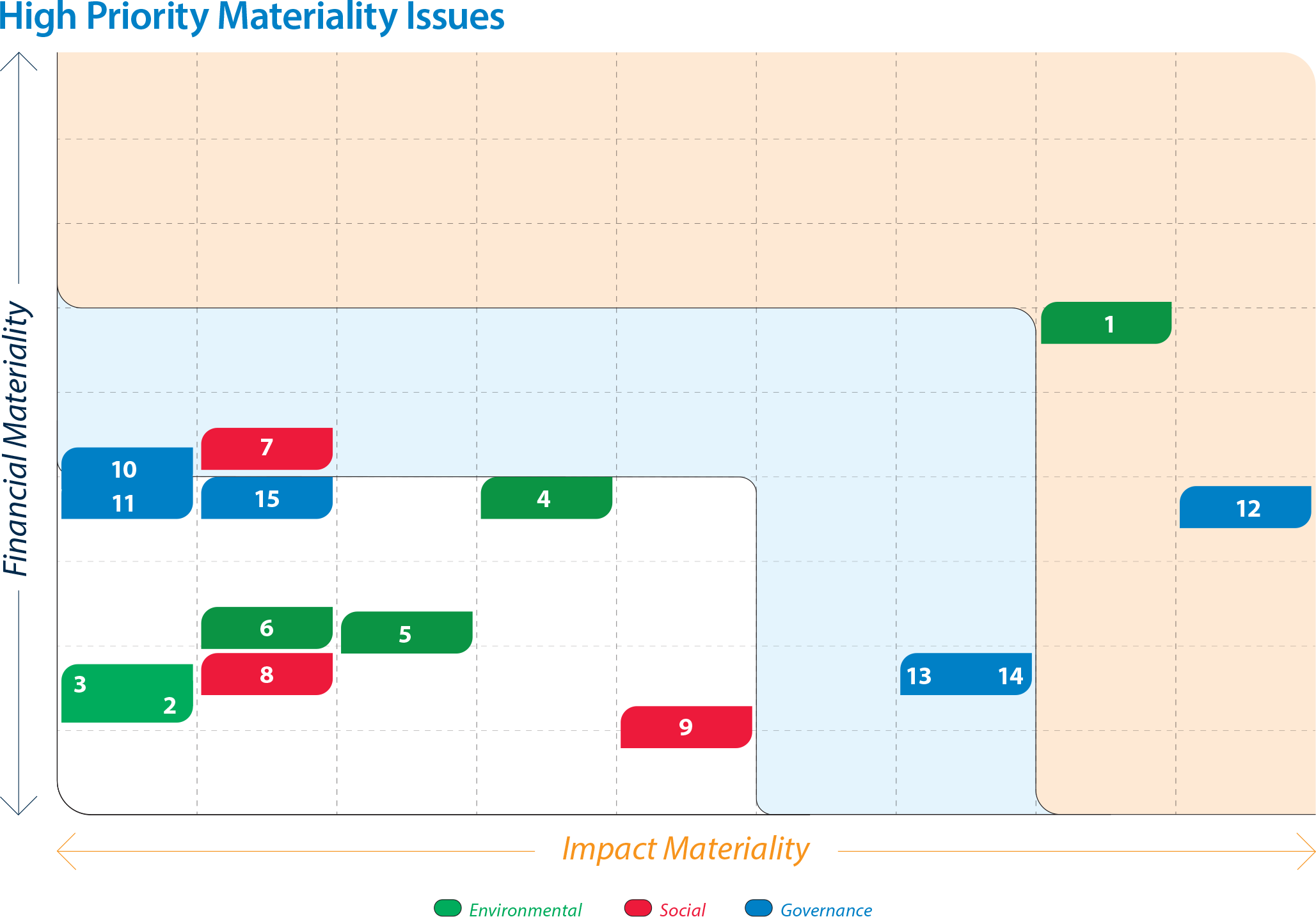
High priority material issues based on independent analysis for Tata Steel on a consolidated basis are as follows:
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Management
Circular Economy/ Recycling of By-products
Water Consumption and Effluent Discharge
Energy Efficiency/ Energy Management
Air Pollution/Air Quality Management
Biodiversity
Occupational Health and Safety
Employee Well-being and Development
Community Support and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)/Building Thriving Communities
Research and Development/ Technology, Product and Process Innovation
Supply Chain Sustainability
Corporate Governance
Business Ethics, Integrity and Transparency
Stakeholder Engagement
Risk Management
| Material issues | Approach | KPIs | Capital linkages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions & Climate Change Management 
|
Tata Steel has set an ambitious target to achieve Net Zero emissions by 2045. Tata Steel has published its strategy to mitigate climate change-related risks in its Climate Change Report as part of Tata Steel’s Integrated Report for FY2023-24. |
|
|
| 2 |
Circular Economy/ Recycling of By-products 
|
Tata Steel is looking at two approaches for value creation from waste and by-products:
|
|

|
| 3 |
Water Consumption and Effluent Discharge 
|
The Company actively implements the 4R principle (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Replenish) to reduce its water footprint across multiple locations. Tata Steel is also exploring other sources of water to replace freshwater and remains dedicated to replenishing the water sources to strive to achieve Water Neutrality. |
|
|
| 4 |
Energy Efficiency/ Energy Management 
|
Tata Steel is committed to energy conservation and enhancing energy efficiency in all its areas of operations by exploring and implementing best available technologies, and by deploying renewable energy projects. |
|
|
| 5 |
Air Pollution/ Air Quality Management 
|
Tata Steel is committed to identifying, assessing, and managing its air emissions to ensure healthy air quality, by investing in the upgradation of pollution control equipment. |
|
|
| 6 |
Biodiversity 
|
Tata Steel aims at integrating biodiversity into its business ecosystem by committing to conserve, enhance and restore biodiversity in all its operations and across the supply chain. |
|
|
| Material issues | Approach | KPIs | Capital linkages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 |
Research and Development/ Technology, Product and Process Innovation 
|
Tata Steel aspires to be among the top 5 global technology leaders in the steel industry and has consistently used technology and innovation to build a rich portfolio of future-ready products and is actively engaged in the development and pilot of various low CO2 steelmaking technologies. |
|
|
| 11 |
Supply Chain Sustainability 
|
Tata Steel has formulated the Responsible Supply Chain Policy to address sustainability in supply chain and regularly assesses its supply chain partners on the policy and organises training and awareness sessions. Multiple initiatives have been taken between Procurement and Supply Chain to bring down Scope 3 emissions. |
|
|
| 12 |
Corporate Governance 
|
Tata Steel has laid a strong corporate governance foundation which is led by an active, well informed and independent Board and supported by Board committees. This is well supported by the Company’s ethical governance framework and the Enterprise Risk Management practices of the Company. |
|
|
| 13 |
Business Ethics, Integrity, and Transparency 
|
Tata Steel strives for global leadership in standards of ethics, based on the strong foundation of Tata values and the Tata Code of Conduct (TCoC) and its principles underpinned by a formalised Management of Business Ethics Framework and commitment to transparency. |
|

|
| 14 |
Stakeholder Engagement 
|
Tata Steel seeks to balance the needs, interests, and expectations of all stakeholders with those of the business through an integrated and inclusive process. Tata Steel also undertakes regular materiality assessment to understand key issues for various stakeholder groups and incorporates those in its broader strategy. |
|
|
| 15 |
Risk Management 
|
Tata Steel has developed the Enterprise Risk Management framework and process derived from COSO (Committee of Sponsored Organisation), ISO 31000:2018 and various inputs from the best practices across industries. The process is uniformly deployed across the organisation and risks arising from the potential material issues are integrated with organisation’s ERM framework. |
|
|